AFL++ Grammar Level Fuzzing on Micro QuickJS
0. 起因
2025.12.23 传奇程序员 Bellard(Qemu、ffmpeg、QuickJS、TCC... 原作者)发布了他的新作品 Micro QuickJS(mqjs),这是一个用于嵌入式系统上的 JS 引擎。既然是用纯 C 语言实现的,应该会有一些内存损坏漏洞吧。
1. 准备 fuzzer
组件
我决定用 AFL++ 来运行模糊测试。AFL++ 直接使用的话,构造的是逐字节的随机输入,其中大多数都是无意义的乱码(即使配合 cmplog 等)。对于特定语言解释器来说,我们希望构造的输入能够真正被执行。编译原理告诉我们,从人类可读字符串到机器可执行的字节码或机器码需要经历至少三个阶段:词法分析、语法分析、语义分析。完全随机的输入无疑连词法分析都很难通过,更别说语法分析语义分析了。如果构造的输入根本没法运行,那我们就无法触及有关 VM 和 GC(垃圾回收释放内存)相关的更有价值的漏洞。
西电网信院在大二有一门选修课就是编译原理,最后的大作业是 C 语言标准库手搓自定义绘图语言编译器,十分带劲。不过据说从 24 级开始这门课🈚️了。
我感觉从 LLVM pass 上手会更有实用价值一些。
而如果配合 Grammar-Mutator,我们就可以实现语法级的 fuzzing。我们只需要提供这个语言的语法的生成式,自动编译成自定义 mutator。AFL 运行时就会调用它来将先前的 seed 转变为 AST,再随机选择 AST 中的节点,根据生成式变异为另一个节点或子树,最后再根据 AST 生成代码作为新的 seed。(具体可以看这篇文章)
当然,编译时 Address Sanitizer 也必不可少(-fsanitize=address)。我试过再加上 UB Sanitizer,但是随便一运行就爆了,难道到处都是 UB?
问题修复
一开始运行 Grammar-Mutator 有时会报错 _pick_non_term_node returns NULL 然后直接退出。不知道为什么它在极罕见情况下会找不到某个非终结符能够用来变异的生成式。
遇到这种情况就不变异吧,直接把整个 AFL 停了真的好吗,,修改代码如下即可:
diff --git a/src/tree_mutation.c b/src/tree_mutation.c
index 68e91f9..62da2ed 100644
--- a/src/tree_mutation.c
+++ b/src/tree_mutation.c
@@ -39,8 +39,10 @@ tree_t *random_mutation(tree_t *tree) {
if (unlikely(node == NULL)) {
// By design, _pick_non_term_node should not return NULL
- perror("_pick_non_term_node returns NULL");
- exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
+ // perror("_pick_non_term_node returns NULL");
+ // exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
+
+ return mutated_tree;
}
@@ -203,9 +205,10 @@ tree_t *splicing_mutation(tree_t *tree) {
if (unlikely(node == NULL)) {
// By design, _pick_non_term_node should not return NULL
- perror("_pick_non_term_node returns NULL");
- exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
+ // perror("_pick_non_term_node returns NULL");
+ // exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
+ return mutated_tree;
}
node_t *parent = node->parent;执行
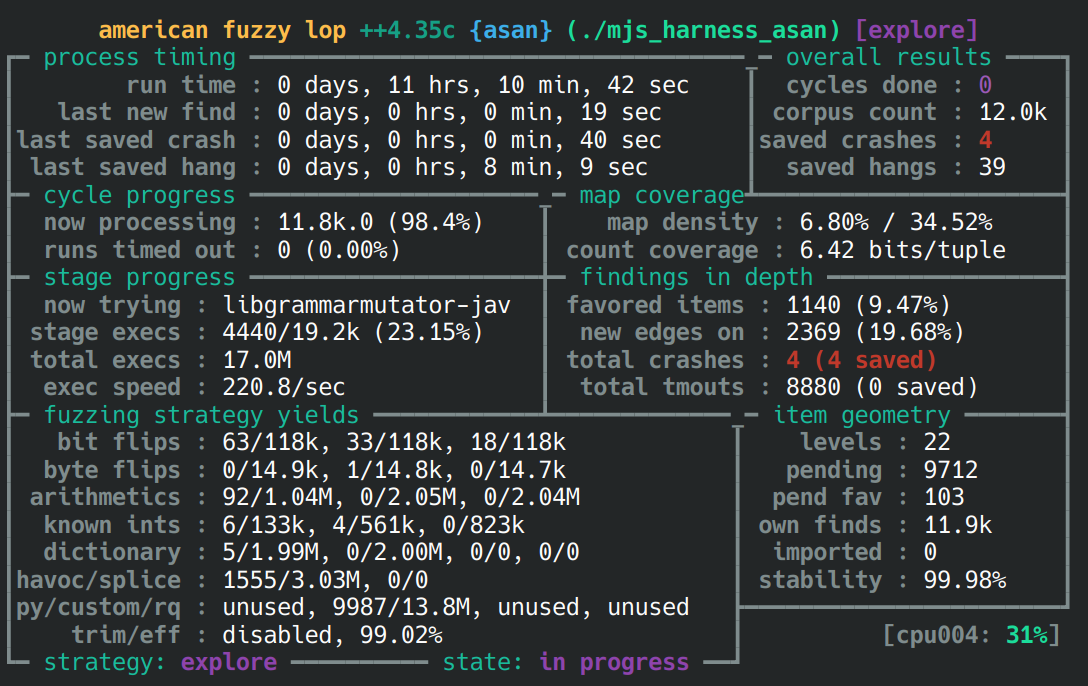
编写 fuzzing harness 用于 persistent mode,同时按照 Grammar-Mutator 的官方文档编译好 mutator library,自动生成初始种子。我们在 aflplusplus/aflplusplus docker container 里用以下参数运行 AFL:
while true; do AFL_DISABLE_TRIM=1 AFL_CUSTOM_MUTATOR_LIBRARY=./libgrammarmutator-javascript.so AFL_USE_ASAN=1 afl-fuzz -i seeds/ -o out/ -b 2 -a text -G 1024 -t 200 -S asan -- ./mjs_harness_asan; sleep 1; done运行过程中我总结了一些经验:
- 我选择关闭 ptrim,因为对于语法级 fuzzing,trim 反而会丢失复杂的结构,使之后的变异难以发现新的分支。
- 加上超时是对的,但是不能太低,跑得慢的 seed 反而更有价值(复杂的 GC 行为)。
- Grammar-Mutator 根据 AST 进行变异像是一个无限深度递归,所以 cycles 几乎不会增长,这是正常的。
2. Fuzzing 结果
大约 11 小时后,第一批 crashes 出现了:
id 000000 内容大概是:
var a = [];
var b = [];
var c = [];
var d = [];
(Infinity**((((a+(((((((((((((((((((((new Float64Array(0,0/0,0,{g: false})))))))))))))))))))))==(~0)))))));
function Float64Array(console, EvalError,Int16Array,Reflect,NaN){
new Float64Array(false,TypeError[[[((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((d.concat([b],{f: []}).concat([b],{f: []}).concat([b],{f: []}).concat([b],{f: []}).concat([b],{f: []}).concat([b],{f: []}).concat([b],{f: []}).concat([b],{f: []}).concat([b],{f: []}).concat([b],{f: []}).concat([b],{f: []}).concat([b],{f: []}).concat([b],{f: []}).concat([b],{f: []}).concat((((--b) >>> -0)),(((--b) >>> -0)),(((--b) >>>
// 暂不完整公开 ...可以看到其中有明显的无限递归,另外还有大量的 concat,这无疑同时给堆和栈带来了巨大的内存分配压力,也就很可能出现 GC 相关的漏洞。
对此,Address Sanitizer 的评价是:
=================================================================
==1599335==ERROR: AddressSanitizer: negative-size-param: (size=-2112)
#0 0x55f81ffe8449 in __asan_memmove (/home/rik/Desktop/crashes/mjs_harness_asan+0x17e449) (BuildId: 44bae498641fcf1516b886c154ce5bcf4f3fdee4)
#1 0x55f8200c1be2 in JS_MakeUniqueString /home/rik/Desktop/fuzzing/mjs-fuzzing/mquickjs/mquickjs.c:2032:5
#2 0x55f8200aab94 in JS_ToPropertyKey /home/rik/Desktop/fuzzing/mjs-fuzzing/mquickjs/mquickjs.c:4193:16
#3 0x55f8200aab94 in JS_Call /home/rik/Desktop/fuzzing/mjs-fuzzing/mquickjs/mquickjs.c:6009:28
#4 0x55f82011a802 in JS_Run /home/rik/Desktop/fuzzing/mjs-fuzzing/mquickjs/mquickjs.c:11799:11
#5 0x55f82003e19b in LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput /home/rik/Desktop/fuzzing/mjs-fuzzing/mquickjs/fuzz_harness.c:140:15
#6 0x55f820038c59 in ExecuteFilesOnyByOne (/home/rik/Desktop/crashes/mjs_harness_asan+0x1cec59) (BuildId: 44bae498641fcf1516b886c154ce5bcf4f3fdee4)
#7 0x55f820038a38 in LLVMFuzzerRunDriver (/home/rik/Desktop/crashes/mjs_harness_asan+0x1cea38) (BuildId: 44bae498641fcf1516b886c154ce5bcf4f3fdee4)
#8 0x55f8200385c6 in main (/home/rik/Desktop/crashes/mjs_harness_asan+0x1ce5c6) (BuildId: 44bae498641fcf1516b886c154ce5bcf4f3fdee4)
#9 0x7f24f4027634 in __libc_start_call_main /usr/src/debug/glibc/glibc/csu/../sysdeps/nptl/libc_start_call_main.h:58:16
#10 0x7f24f40276e8 in __libc_start_main /usr/src/debug/glibc/glibc/csu/../csu/libc-start.c:360:3
#11 0x55f81feef3e4 in _start (/home/rik/Desktop/crashes/mjs_harness_asan+0x853e4) (BuildId: 44bae498641fcf1516b886c154ce5bcf4f3fdee4)
0x7f24f0c4f8b8 is located 327864 bytes inside of 4194304-byte region [0x7f24f0bff800,0x7f24f0fff800)
allocated by thread T0 here:
#0 0x55f81ffeb905 in malloc (/home/rik/Desktop/crashes/mjs_harness_asan+0x181905) (BuildId: 44bae498641fcf1516b886c154ce5bcf4f3fdee4)
#1 0x55f82003cee9 in LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput /home/rik/Desktop/fuzzing/mjs-fuzzing/mquickjs/fuzz_harness.c:112:21
#2 0x55f820038c59 in ExecuteFilesOnyByOne (/home/rik/Desktop/crashes/mjs_harness_asan+0x1cec59) (BuildId: 44bae498641fcf1516b886c154ce5bcf4f3fdee4)
SUMMARY: AddressSanitizer: negative-size-param (/home/rik/Desktop/crashes/mjs_harness_asan+0x17e449) (BuildId: 44bae498641fcf1516b886c154ce5bcf4f3fdee4) in __asan_memmove
==1599335==负数 size?
过了一会,又出现了七百多个崩溃,我想是时候开始分析了。
3. 分析 crashes
Micro QuickJS 的 GC 过程如下:
先将整个堆扫描一遍来标记需要释放的对象(JS_MTAG_FREE),
/* 'size' is in bytes and must be multiple of JSW and > 0 */
static void set_free_block(void *ptr, uint32_t size)
{
JSFreeBlock *p;
p = (JSFreeBlock *)ptr;
p->mtag = JS_MTAG_FREE;
p->gc_mark = 0;
p->size = (size - sizeof(JSFreeBlock)) / sizeof(JSWord);
}然后在 JS_GC2 中使用 Jonkers 算法来释放内存(gc_compact_heap)。具体来说,就是把所有不是 JS_MTAG_FREE 标记的对象都向低地址移,填补所有 JS_MTAG_FREE 对象带来的空洞。
/* pass 2: update the threaded pointers and move the block to its
final position */
new_ptr = ctx->heap_base;
ptr = ctx->heap_base;
while (ptr < ctx->heap_free) {
gc_update_threaded_pointers(ctx, ptr, new_ptr);
size = get_mblock_size(ptr);
if (js_get_mtag(ptr) != JS_MTAG_FREE) {
if (new_ptr != ptr) {
memmove(new_ptr, ptr, size);
}
new_ptr += size;
}
ptr += size;
}
ctx->heap_free = new_ptr;一个很关键的问题是,这样的 GC 有可能会移动对象的位置,所以 GC 的下一步是修改引用方的指针到移动后的位置。不在 JS VM 栈中的对象指针(例如在裸 C 数组里的 JS 对象指针)就无法被追踪到,它们就会立刻沦为垂悬指针。所以在编写 mqjs 期间需要时刻注意哪些函数可能触发 GC,并将临时变量推入 JS VM 栈中。
这几百个崩溃几乎都是因为没有注意到可能 GC 的函数导致的。例如 2 中提到的崩溃,
static JSValue JS_MakeUniqueString(JSContext *ctx, JSValue val) {
// ...
arr = JS_VALUE_TO_PTR( ctx->unique_strings);
val1 = find_atom(ctx, &a, arr, ctx->unique_strings_len, val);
if (!JS_IsNull(val1))
return val1;
JS_PUSH_VALUE(ctx, val);
is_numeric = js_is_numeric_string(ctx, val);
JS_POP_VALUE(ctx, val);
if (is_numeric < 0)
return JS_EXCEPTION;
/* not found: add it in the table */
JS_PUSH_VALUE(ctx, val);
new_tab = js_resize_value_array(ctx, ctx->unique_strings,
ctx->unique_strings_len + 1);
JS_POP_VALUE(ctx, val);
if (JS_IsException(new_tab))
return JS_EXCEPTION;
ctx->unique_strings = new_tab;
arr = JS_VALUE_TO_PTR( ctx->unique_strings);
memmove(&arr->arr[a + 1], &arr->arr[a],
sizeof(arr->arr[0]) * (ctx->unique_strings_len - a));
// ...
}可以看到 JS_MakeUniqueString 首先从 ctx->unique_strings 中搜索(find_atom)相同字符串的索引(a)。这是一种常见的优化,在创建任何字符串前都在一个字符串表里检查有没有重复字符串,如果有就直接使用它如果没有再分配新空间并插入表中,避免重复浪费内存。但是由于 ctx->unique_strings_len 在 find_atom 和 memmove 之间减小了(被 GC 清理了一部分),所以 ctx->unique_strings_len - a 变成了负数!(a 应该永远小于 ctx->unique_strings_len。)其中 js_is_numeric_string 和 js_resize_value_array 都有可能触发 GC(主要是 js_is_numeric_string)。
按照以上思路,我们还能找到其他 GC UAF 漏洞,甚至可利用的漏洞。事实上,我们可以修改 mqjs 源码,使其在每次申请内存前都执行一次 GC,这样能更高效地挖掘出类似的漏洞,无需等待 AFL 随机出有 GC 压力的 seed。(这应该是一个通用的技巧)
4. 利用
...
5. 修复
对于 2 中提到的崩溃,比较简单的修复方案就是在 memmove 前再执行一次 find_atom 定位插入位置。另外 js_is_numeric_string 也不应该需要 O(n) 空间复杂度。
...
在 QuickJS-NG 也可以通过相同方案找到有意义的漏洞。